Prostatitis is a dangerous, but, unfortunately, very common disease of the male genitourinary system. The disease used to occur mainly in older men, but today urologists are increasingly diagnosing this disease in young patients. Every man who cares about his health needs to know what types of prostatitis are and how they manifest themselves.
Reasons for the development of prostatitis

Sharp hypothermia of the prostate is the "safest" way to earn prostatitis.
Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate. This disease must be diagnosed and treated in a timely manner, otherwise serious consequences are possible.
The causes of this disease are divided into two large groups - infectious and non-infectious. The contagious causes of this disease include:
- opportunistic pathogens that are always present in the human body;
- Mushrooms;
- sexually transmitted bacteria;
- viruses;
- mycobacteria.
The opportunistic causative agents of this disease are Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, since most infectious prostatitis is caused by these pathogens. They reach the prostate from the gastrointestinal tract with the blood or lymph movement. The disease can also be caused by the penetration of pyogenic bacteria (pneumococci, staphylococci) from the urethra or through the hematogenous route.
Most often, fungi that cause prostatitis are yeast microflora of the genus Candida. Infection with this fungus can be sexual, but Candida is an important part of the normal human microflora, so it can enter the prostate from other organs and systems. In rare cases, fungal prostatitis is caused by mold.
Inflammation of the prostate can be caused by infection with syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and other infections transmitted through unprotected sex.
In rare cases, viruses become the cause of the disease. So, prostatitis can develop against the background of influenza or SARS, when the virus spreads throughout the body with blood flow. Prostate tuberculosis is isolated separately. This is a dangerous disease associated with infection of the organ with Koch's bacillus, the causative agent of tuberculosis.
Non-infectious causes of prostate inflammation:
- stagnation of prostate secretion;
- violation of blood circulation and outflow of lymph from the pelvic organs;
- hypothermia of the genitals;
- varicose veins.
In general, non-infectious prostatitis is often called the "disease of office workers" because its development is directly related to physical inactivity.
risk factors

If earlier the main risk group for the development of this disease were men over 50 years old, today there are much more risk factors, so young men aged 23-25 years are increasingly faced with prostatitis. The risk of prostate inflammation increases due to:
- lack of regular sex life;
- sedentary work and hypodynamia;
- endocrine disorders;
- hormonal disorders;
- hypothermia;
- emphasize;
- malnutrition;
- Bad habits;
- unprotected sex.
The lack of sex life is the main enemy of the prostate. At the same time, however, too intense a sex life also damages this organ. If, with prolonged abstinence, inflammation can be triggered by stagnation of the prostatic secretion, which comes out during ejaculation, then a rich sex life exhausts the prostate, and with it also provokes the development of prostatitis.
A man's body needs regular physical activity. Otherwise, blood flow to the pelvic organs deteriorates, which leads to swelling of the prostate and disruption of the trophism of the tissues of the organ, which, in turn, is the main cause of the development of non-infectious inflammation the prostate.
Also, risk factors include a decrease in immunity, promiscuity, various diseases of the genitourinary system, which can be a potential source of infection.
Classification of prostatitis
To understand what prostatitis is, in the first place, the classification of diseases will help. However, it is not recommended to diagnose yourself by describing the symptoms. At the first signs of discomfort, you should consult a urologist. It should be understood that different types of prostatitis manifest themselves in different ways, but all of them pose a threat to men's health if not treated in a timely manner.
Regardless of the form of prostatitis, treatment should begin as early as possible. Early diagnosis and timely therapy is a chance to get rid of the disease in a few weeks without the risk of complications.
Prostatitis is classified according to the type of inflammation and the degree of involvement of the prostate tissue in the pathological process. Each form of the disease has specific signs that are identified during the examination. So, the results of the analysis of the prostate secretion, which should be taken by all men with suspected prostatitis, will best provide information about the nature of the disease.
What is acute prostatitis?

Before considering the specific forms of the inflammatory process in the prostate, it is necessary to understand what prostatitis is by type of course. There are two main forms - acute and chronic inflammation.
Acute prostatitis is a rapidly spreading inflammation in the prostate. Most often it is a disease caused by pathogens. However, the non-infectious form of the disease can also occur acutely, for example during the initial manifestation.
Acute prostatitis is characterized by vivid symptoms. Men complain of severe disturbances in urination, severe pain radiating to the perineum, lower back and anus. Symptoms increase when trying to urinate and ejaculate.
Features of chronic prostatitis
The chronic form of the disease results from acute prostatitis. This type of prostatitis in men has less pronounced symptoms and is primarily associated with the lack of treatment or inadequate therapy for acute prostatitis. The pathology is characterized by sluggish inflammation, which can sometimes worsen.
Symptoms of the disease: weak stream of urine, sluggish erection, weak excitement. With chronic prostatitis, the nightly urge to go to the toilet increases, during defecation he feels discomfort in the prostate, which is manifested by a feeling of squeezing or bursting of the organ.
With hypothermia or a decrease in immunity, the symptoms intensify, pain and spasms in the bladder appear, and the urge to go to the toilet becomes more frequent.
Bacterial prostatitis: features and symptoms
One of the most common types of the disease is bacterial prostatitis. It is caused by the invasion of various bacteria into the prostate. Most often, the causative agent is Escherichia or Pseudomonas aeruginosa or other opportunistic bacteria that inhabit the human body.
The main reasons for its development are a decrease in immunity, severe stress, smoking and other conditions that weaken the body.
Bacterial prostatitis is manifested by the following symptoms:
- pain and pain when urinating associated with irritation of the urethra by bacteria invading from the prostate;
- high body temperature;
- Symptoms of general intoxication: nausea, dizziness, weakness;
- pain in the perineum;
- Excretion of blood in the urine.
This form of the disease progresses quickly and can lead to a prostate abscess. When the first symptoms appear, you should immediately make an appointment with a specialist.
Infectious prostatitis
Infectious means prostatitis caused by bacteria, fungi, viruses. In fact, bacterial prostatitis is a type of infectious inflammation. This type of pathology has the same symptoms as bacterial inflammation.
The infectious form of the disease can occur in acute and chronic forms. As a rule, the chronic form of the disease develops due to complications or improper treatment of an acute inflammatory process.
Viral prostatitis

Acute respiratory viral infection can serve as a catalyst for the development of viral prostatitis
The most dangerous and least studied form of infectious prostatitis is viral inflammation. It can be triggered by herpes, the human papilloma virus, the causative agent of measles, rubella, influenza. Often, inflammation of the prostate occurs against the background of the spread of the causative agent of the usual SARS.
The problem with viral prostatitis is that antibiotic therapy is ineffective, and antiviral agents do not penetrate well into the tissues of the prostate gland.
As a result, long therapy with antivirals and immunomodulators is required, after which the disease is likely to become chronic and treatment with other drugs will continue. This form of prostatitis often leads to infertility at a young age.
fungal prostatitis
This is a rare form of the disease caused by a fungus of the genus Candida. The main feature of this type of inflammation is the almost complete absence of symptoms in the initial stages. Thus, fungal prostatitis does not manifest itself in an acute form, but immediately turns into a chronic disease.
Purulent inflammation of the prostate
This is the most severe and dangerous form of infectious inflammation caused by pyogenic bacteria. The pathology proceeds in an acute form, which is manifested by high body temperature and the release of purulent masses from the urethra. The disease can lead to an abscess of the prostate, which requires urgent hospitalization and surgical intervention, otherwise the abscess can rupture and become infected with purulent masses of blood.
Calculous form of inflammation
Stones or stones can form in the prostate. They are deposits of phosphates and calcifications in the walls of the organ. Stones irritate prostate tissue and cause an inflammatory response. This form of the disease is characterized by the passage of blood in the urine and a sharp pain during defecation due to the movement of salt deposits due to muscle tension and damage to the prostate tissue. This form of the disease is experienced by older men. In addition, calculous prostatitis is considered a complication of congestive prostatitis, which the man has not treated.
diagnosis
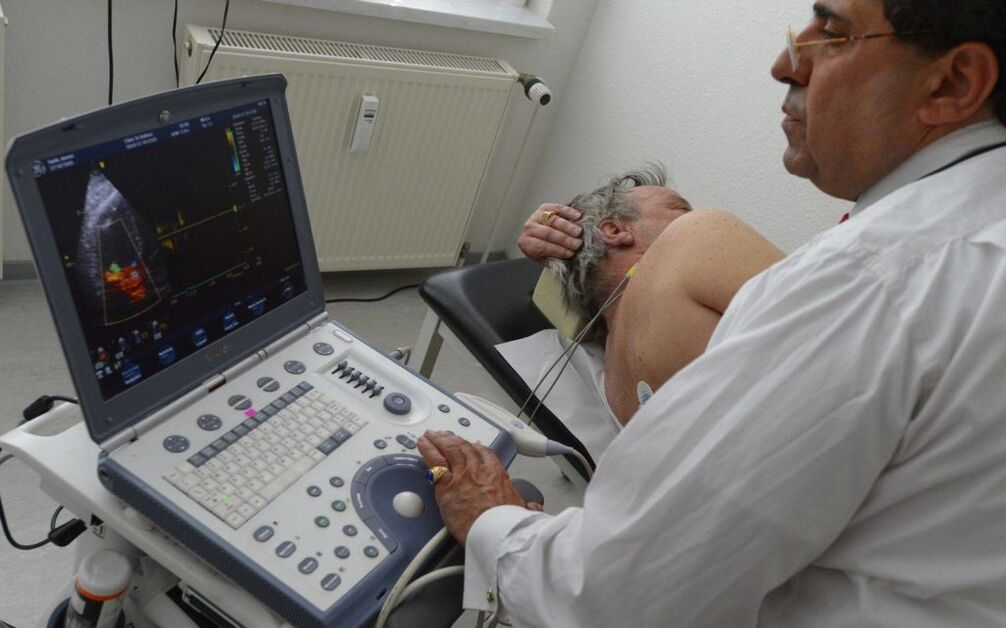
Having understood the types of prostatitis in men and the symptoms of various types of inflammation, it becomes clear that the diagnosis should be made exclusively by a specialist. At the first signs of discomfort, it is necessary to contact a urologist and undergo examinations. A palpation of the prostate, an analysis of the prostatic secretion and an ultrasound examination of the organ are used to make the diagnosis.
The cause of the inflammation is determined by the composition of the prostate juice, its consistency and quantity. Ultrasound is performed to exclude calculous prostatitis. Based on the results of these tests, a diagnosis is made and an optimal treatment regimen is prescribed.
treatment of inflammation
Signs and symptoms of prostatitis depend on the type of condition. Treatment is selected for each patient individually, depending on the nature of the inflammatory process. In general, all bacterial inflammatory processes are treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics with an antimicrobial effect. To treat a viral disease, antiviral drugs and drugs to strengthen the immune system are used. The fungal form of the disease requires the use of special drugs - antifungal drugs.
To eliminate non-infectious inflammation, so-called prostate biostimulators are used. These are drugs that improve the trophism of the tissues of the inflamed organ, dilute the prostatic secretion and stimulate its outflow. These drugs improve the body's functions.
In addition, symptomatic treatment is prescribed. In the acute form of the disease, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used, which relieve pain and fever. If a man has severe problems with urination, drugs that relax the muscles of the bladder and urethra are used - alpha-blockers.
In addition, herbal diuretics, suppositories that improve blood flow to the gland, anti-inflammatory drugs of natural composition and other groups of drugs are used.
It is important to remember that self-medication can cause great harm to health. Drug therapy should only be prescribed by the attending physician.
How to prevent the development of the disease?

To prevent the disease, you should undergo regular medical examinations.
Prostatitis prophylaxis is a hot topic for all men. For a healthy prostate you must:
- treat all diseases in a timely manner;
- always dress appropriately for the weather and avoid hypothermia of the genitals;
- Take care of your health and use contraception.
- lead an active lifestyle;
- play a sport;
- refuse from bad habits;
- Eat properly.
For prevention, all men are advised to consume pumpkin seeds in small amounts as this product is a natural prostate protector.
In addition, all men over the age of 40 should see a urologist every year, even without symptoms.